Abstract
Diabetic people, especially those with diabetes (type 2), have a two- to three-fold greater chance of developing coronary artery disease (CAD) compared to non-diabetics. By assessing the angiograms of diabetic as well as non-diabetic individuals, the current study sought to determine the impact of diabetes mellitus (DM) on the degree and intensity of CAD. This cross-sectional study included 138 male patients out of 1246 patients who underwent coronary angiography for suspected CAD. Type 2 diabetes had been diagnosed in 78 of these patients. fourteen diabetic patients were not found to have CAD. Sixty-four (46.37%) of the diabetic patients and sixty (43.47%) of the non-diabetic patients were found to have CAD and were then examined in the current investigation. Type-2 diabetes demonstrated significantly greater hypertension and age disparities than non-diabetics. Diabetes patients had an increased prevalence of multi-lesion, multivessel, extensive, and relatively small vessel disease than people without diabetes. The left circumflex artery was indeed the coronary artery that was typically frequently affected in diabetes individuals. People who have diabetes (n = 41; 64.7%) had substantially (P = 0.02) greater rates of triple vessel involvement. The structure of the coronary arteries is significantly impacted by diabetes type 2 which is also linked to hypertension, age, and an increased risk of multivessel and severe CAD.
Key Words
Type-2 Diabetes, Coronary Heart Disease, Coronary Artery Disease (CAD), Hypertension, Angiography
Introduction
Globally, cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) continue to be the leading cause of mortality, contributing to about 10% of the worldwide illness and 30% of world death. Globally death rates from coronary heart diseases (CHDs) and CVDs were correspondingly 29.3% and 13.1% in 2005. In Pakistan, coronary artery disease (CAD) is currently the main cause of mortality, and its incidence is comparable to that of the industrialized nations. Worldwide, a variety of risk factors, including diabetes mellitus (DM), are related to a higher frequency and death from CHDs (Mendis et al., 2011; WHO. 2002; WHO. 2008; WHO. 2007). DM is, after cardiovascular illnesses, the second most prevalent reason for non-communicable disorder death globally. Specifically, in type 2 diabetes where atherosclerosis is frequent, diabetes has a probability of developing CAD that is 2-3 times greater than that of non-diabetic individuals. After the findings of Seegen J. Der, which highlighted the greater prevalence and death of CAD among diabetes patients, a relationship involving DM and CHDs was discovered in 1870 (WHO. 2005; Nathan et al., 1997; Hegde et al., 2014).
Diabetes-related cardiac activity often takes the form of CAD, with cardiac autonomic neuropathy and diabetic cardiomyopathy occurring less frequently. In autopsy and angiographic-based research, a link between more severe CAD and DM has already been noted using coronary computational angiography with multiple slices (Ross, 1996; Erling et al., 1998). Diabetic individuals have both a higher prevalence and a much more serious condition of coronary atherosclerosis. Diabetes patients have a penetration rate of CAD ranging from 9.5% to 55%. The fact that diabetic individuals with CAD had increased Gensini scores during angiography is also widely established. More people with diabetes (95%) exhibited aberrant Gensini scores when diabetes participants are examined. Very few studies have been conducted in Pakistan regarding the CAD and angiographic characteristics of patients with CAD (Falk, 1991; Nathan et al., 1997; Thripaty, 2001; Rlos, n.d). By assessing the angiograms of diabetic as well as non-diabetic individuals, the current study sought to determine the impact of DM on the degree and intensity of CAD.
Material and Methods
This study included a total of 138 male patients out of 1246 patients who underwent coronary angiography for suspected CAD between April 2021 and March 2022 at Hayatabad Medical Complex, Peshawar, and Saidu Teaching Hospital, Swat in Pakistan. Among these patients, 78 were diagnosed with type 2 diabetes. Fourteen diabetic patients were found to be free of CAD. Subsequently, 64 (46.37%) diabetic patients and 60 (43.47%) non-diabetic patients with CAD were included in the current investigation.
Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
The study included male patients who underwent coronary angiography for suspected CAD. Patients with type 2 diabetes were included, while those with type 1 diabetes, valvular heart disease, left ventricular hypertrophy, congestive heart failure, and cardiomyopathy were excluded.
Angiography Procedure
Coronary angiography (CAG) and left ventriculography were performed using Judkin's method through a femoral route and a customized Seldinger method with nonionic dyes. Standard images from multiple angles were captured for examination. The severity and extent of coronary artery disease were visually assessed through comprehensive CAG evaluation. Lesion structural parameters were examined according to hospital policy. A positive CAG was recorded when coronary artery stenosis reached 50% or higher, while a negative CAG indicated stenosis below 50%.
Statistical Analysis
After data collection, a statistical analysis was conducted to determine the relevance of the findings. Parametric and non-parametric results were reported as percentages (%) and means, respectively. Pearson's chi-square test, unpaired Student's t-test, and z-test were employed to assess the significance of differences between the two groups. A p-value of 0.05 or less was considered statistically significant.
Ethical Statement
The research study was approved by the research ethics committee of both institutes conducting the study. Prior to participating in the trial, each patient provided written informed consent.
Results
The research participants' ages ranged from 27 to 75 years, with a
mean age ± SD of 57.52 ± 10.2 years. The difference in average age between
diabetes patients and non-diabetics (58.3 ± 8.19 years vs. 56.12 12.18
years) was statistically significant (P = 0.012). The research sample's average
BMI and waist measurements were 29.11 ± 6.12 and 104.89 ± 11.87 cm,
respectively. Moreover, diabetic individuals had considerably more hypertension
(70.31%) than non-diabetics (58.33%). There were no significant connections
between several sociodemographic factors. Diabetes patients had a greater
incidence of extensive, multisession, multivessel, and smaller-vessel illnesses than people
without diabetes (Table 1). Diabetes patients were more inclined to have triple
vascular involvement (n = 41; 64.7%), while non-diabetics were more likely to
have single as well as double artery involvement (n = 13, 21.65%, and n = 19,
31.68%) correspondingly (table 2).
Table 1
Diabetes and Specific Socio-demographic traits
along with other Epidemiological factors are Associated
|
Components |
Non-Diabetics |
Diabetics |
P value |
||
|
(n) |
%a |
(n) |
%a |
||
|
Age |
(Mean age ± SD = 57.52
± 10.2) |
||||
|
Below 50 |
21 |
35.0 |
6 |
9.37 |
0.018 |
|
50-60 |
13 |
21.66 |
23 |
35.93 |
|
|
61-70 |
16 |
26.67 |
26 |
40.62 |
|
|
Above 70 |
10 |
16.67 |
9 |
14.08 |
|
|
Body Mass Index (BMI) |
(Mean BMI ± SD
= 29.11 ± 6.12) |
||||
|
<18 |
0 |
0.0 |
0 |
0.0 |
0.129 |
|
18 - 23 |
11 |
18.33 |
6 |
9.37 |
|
|
24 - 29 |
19 |
31.67 |
25 |
39.06 |
|
|
Above 30 |
30 |
50.0 |
33 |
51.57 |
|
|
Waist circumference |
(Mean ± SD =104.89 ± 11.87) |
||||
|
Normal |
15 |
25.0 |
12 |
18.75 |
0.378 |
|
High |
45 |
75.0 |
52 |
81.25 |
|
|
Smoking |
|||||
|
No |
8 |
13.33 |
4 |
6.25 |
0.18 |
|
Yes |
52 |
86.67 |
60 |
93.75 |
|
|
Alcohol |
|||||
|
No |
51 |
85.0 |
61 |
95.32 |
0.068 |
|
Yes |
9 |
15.0 |
3 |
4.68 |
|
|
Family history of CAD |
|||||
|
No |
46 |
76.67 |
52 |
81.25 |
0.872 |
|
Yes |
14 |
23.33 |
12 |
18.75 |
|
|
Hypertension |
|||||
|
No |
25 |
41.67 |
19 |
29.69 |
0.26 |
|
Yes |
35 |
58.33 |
45 |
70.31 |
|
|
Multivessel disease |
22 |
36.67 |
38 |
59.37 |
<0.05 |
|
Multilesion disease |
29 |
48.33 |
44 |
68.75 |
<0.05 |
|
Extensive disease |
7 |
11.67 |
33 |
51.56 |
<0.05 |
|
Smaller vessel disease |
23 |
38.33 |
58 |
90.62 |
<0.05 |
Table 2
Those with and without Diabetes have different numbers of Coronary
Arteries Affected
|
Vessels (n) |
Non Diabetic |
Diabetic |
P value |
||
|
No |
% |
No |
% |
|
|
|
No |
4 |
6.67 |
2 |
3.12 |
0.02 |
|
Single |
13 |
21.65 |
8 |
12.5 |
|
|
Double |
19 |
31.68 |
13 |
20.31 |
|
|
Triple |
24 |
40.0 |
41 |
64.07 |
|
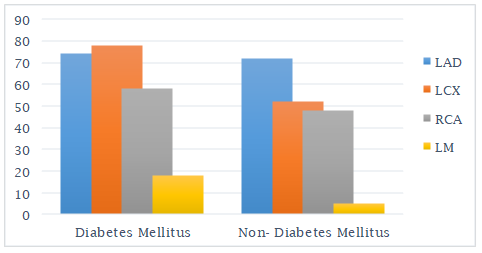
More diabetic patients than non-diabetic patients had left main and
left circumflex coronary artery disease. The left circumflex artery (LCX), left
descending artery (LAD), right coronary arteries (RCA), and left major (LM)
coronary arteries were the most often affected coronary arteries in diabetes
individuals. Nevertheless, among non-diabetic individuals, the left descending
artery (LAD), the left circumflex artery (LXC), the right coronary arteries
(RCA), and the left major (LM) coronary arteries were the most often
damaged coronary arteries (Figure 1).
Figure 1
Comparison of diabetic patients and nondiabetic patients circumflex coronary artery disease
Discussion
There is a global epidemic of DM. Both in wealthy and emerging nations, it is becoming more and more common. The principal reason for death and morbidity among diabetes people, CHD is extremely common. It is generally known that people with diabetes have more aggressive coronary artery lesions at angiography, which is a critical risk factor for the frequency of CAD (Parvin et al., 2015; Srinidhi et al., 2014). This research examined people with diabetes with individuals who did not have diabetes and examined numerous risk variables, clinical profiles, and angiographic patterns.
This study found that the mean age of diabetes was substantially greater than that of non-diabetics. This result is comparable to those that were recorded in Gaza Palestine (2010 and 2013), Bangladesh (2009), Brazil (1993 and 2001), India (2014), and Albania (2012 and 2014) (Sousa et al., 2006; Jamee et al., 2015; Zera et al., 2015; Parvin et al., 2015; Mohammad, 2014). Further studies conducted in Nablus, Palestine (2009), Milan, Italy (2007 and 2008) Nepal (2011 and 2013), and Baghdad, Iraq (2009) found no appreciable age differences (Andreini et al., 2010; Dubey et al., 2014; Kadhim, 2013; Hadamitzky et al., 2010). Diabetes and hypertension were highly correlated. This result is consistent with research conducted in Bangladesh (2009) and Germany (2010) (Wu & Wang, 2002). In comparison to non-diabetic individuals, diabetes patients showed higher rates of multivessel disease (59.37% against 36.67%), multilesion disease (68.75% compared 48.33%), severe disease (51.56% against 11.67%), and small vessel disease (90.62% compared 38.33%). This discovery is comparable to that
which Wang described (2002) (Mahalle et al., 2014).
This study found a larger percentage of triple coronary arteries involved in diabetic individuals, which is consistent with reports from Pakistan, India, and Baghdad between 2008 and 2009 (Hussein, 2011; Ahmed et al., 2015; Krul et al., 2014). This study found a substantial correlation between diabetes patients and critical lesions in the LCX, which is consistent with findings from studies by Sidhu et al., (2019).
Conclusion
The structure of the coronary arteries is significantly impacted by type 2 diabetes, which is also linked related age, hypertension, and a greater prevalence of multivessel and severe CAD than in patients without diabetes. In this study, individuals with diabetes showed a greater prevalence of triple CAD and significant lesions in the LCX artery. These results could be helpful in the future expansion of treatment approaches.
References
- Ahmed, J., Rathi, N., Alam, M. A., Baloch, Z., Munaf, A., Maheshwari, B., Komal Lohana, & Memon, F. (2015). Acute myocardial infarction; a comparative study to assess the angiographic changes in diabetic and non- diabetic patients. The Professional Medical Journal, 22(8), 996–1000. https://doi.org/10.29309/tpmj/2015.22.08.1144
- Andreini, D., Pontone, G., Bartorelli, A. L., Agostoni, P., Mushtaq, S., Antonioli, L., Cortinovis, S., Canestrari, M., Annoni, A., Ballerini, G., Fiorentini, C., & Pepi, M. (2010). Comparison of the diagnostic performance of 64-slice computed tomography coronary angiography in diabetic and non-diabetic patients with suspected coronary artery disease. Cardiovascular Diabetology, 9(1), 80. https://doi.org/10.1186/1475-2840-9-80
- Dubey, L., Guruprasad, S., & Subramanyam, G. (2014). Relationship between type 2 diabetes mellitus and coronary artery lesion characteristics: a single centre study. Nepalese Heart Journal, 10(1), 20–22. https://doi.org/10.3126/njh.v10i1.9742
- Erling F, Valentine F, Predimank S (1998) Interrelationship between atherosclerosis and thrombosis; In Verstrate M, Fuster V, Topol E J, Ed. Cardiovascular thrombosis. Second ed New York, Lippincott Raven: 28- 35. https://doi.org/10.1016/0002-9149(91)90382-u.
- Falk, E. (1991). Coronary thrombosis: Pathogenesis and clinical manifestations. The American Journal of Cardiology, 68(7), B28–B35. https://doi.org/10.2337/dc09-2104
- Hadamitzky, M., Hein, F., Meyer, T., Bischoff, B., Martinoff, S., Schomig, A., & Hausleiter, J. (2010). Prognostic Value of Coronary Computed Tomographic Angiography in Diabetic Patients Without Known Coronary Artery Disease. Diabetes Care, 33(6), 1358– 1363.
- Hegde, S. S., Mallesh, P., Yeli, S. M., Gadad, V. M., & M, G. P. (2014). ComComparativegiographic profile in diabetic and non-diabetic patients with acute coronary syndrome. Journal of cliClinicald diagnostic research: CDR, 8(9), MC07– MC10.
- Hussein, M. F. (2011). Clinical and angiographic findings in diabetic versus non-diabetic Iraqi patients with ischemic heart disease (A single centre experience). The Iraqi Postgraduate Medical Journal, 10(3), 339-346.
- Jamee, A., Abed, Y., Ramadan, M., El-Rabia, K., Nasser, G., & Hijazi, M. (2015). Impact of Diabetes Mellitus on Coronary Artery Disease in Women Attending Coronary Angiography in Gaza- Palestine: An Observational Study. Cardiology and Angiology: An International Journal, 4(1), 10– 18.
- Kadhim, A. R., Strak, S. K., & Hazaa, M. A. (2013). Coronary angiographic findings in diabetic patients versus non-diabetics with coronary heart disease. Al-Kindy Col Med J 9(1), 23-30.
- Krul, G., Bogaard, K., Knol, R. J. J., Albert, Knaapen, P., Cornel, J. H., & van. (2014). Coronary artery disease in patients with atypical chest pain with and without diabetes mellitus assessed with coronary CT angiography. BMJ Open Diabetes Research and Care, 2(1), 1–9.
- Mahalle, N., Garg, M. K., Naik, S. S. & Kulkarni, M. V. (2014) Association of metabolic syndrome with the severity of coronary artery disease. Indian Journal of Endocrinology and Metabolism, 18(5), 708– 708.
- Mendis, S., Puska, P., & Norrving, B. (2011). Global atlas on cardiovascular disease prevention and control.
- Mohammad, H. N. (2014). Cardiovascular diseases and risk factors among diabetic patients in Nablus district, West Bank, Palestine: Case-control study. M.Sc thesis. An-Najah National University.
- Nathan, D. M., Meigs, J., & Singer, D. E. (1997). The epidemiology of cardiovascular disease in type 2 diabetes mellitus: how sweet it is … or is it? The Lancet, 350(S1), S4–S9.
- Parvin, T., Haque, K. S., Siddique, M. A., Habib, S. A., Rahman, M., Rahman, M. H., ... & Hoque, M. H. (2014). Angiographic Severity of Coronary Artery Disease in Diabetic and Non-Diabetic Patients in a Tertiary Care Centre. University Heart Journal, 10(1), 13– 17.
- Rlos, M. (n.d). Cardiac complications in diabetes. World Book of Diabetes in Practice 2: 169
- Ross, R. (1996). Atherosclerosis — an inflammatory disease. Fibrinolysis, 10, 44.
- Sidhu, N. S., Wander, G. S., Monga, A., & Kaur, A. (2019). Incidence, Characteristics and Atherosclerotic Involvement of Coronary Artery Anomalies in Adult Population Undergoing Catheter Coronary Angiography. Cardiology Research, 10(6), 358–368.
- Sousa, J. M., Herrman, J. L., Teodoro, M., Diogo, S., Terceiro, B. B., Paola, A. A., & Carvalho, A. C. (2006). Comparação da coronariografia de mulheres diabéticas e não-diabéticas com sÃndrome coronariana aguda sem supradesnivelamento de ST [Comparison of coronary angiography findings in diabetic and non-diabetic women with non-ST- segment-elevation acute coronary syndrome]. Arquivos brasileiros de cardiologia, 86(2), 150–155. h
- Srinidhi, S. H., Mallesh, P., Yeli, S. M., Veeranna, M. G., & GiriPunja, M. (2014). Comparative angiographic profile in diabetic and non- diabetic patients with acute coronary syndrome. Journal of Clinical and Diagnostic Research 8(9), 7-10.
- Thripaty, B. B. (2001). Complications of diabetes: API textbook of medicine, 6th Edn. Association of Physicians of India: 1005- 1007.
- WHO. (2002). Reducing risks, promoting healthy life. WHO Report.
- WHO. (2005). Preventing chronic diseases–A vital investment. Geneva.
- WHO. (2007). Prevention of cardiovascular disease: Guidelines for assessment and management of total cardiovascular risk. Geneva:
- WHO. (2008). World health statistics 2008. Geneva.
- Wu, T.-G., & Wang, L. (2002). Angiographic characteristics of the coronary artery in patients with type 2 diabetes. Experimental and Clinical Cardiology, 7(4), 199–200.
- Zera, E., Xinxo, S., & Lezha, M. (2015). Comparison of In-Hospital Outcome of Acute Myocardial Infarction in Patients with vs without Diabetes Mellitus in Durres Population. Cardiology and Angiology: An International Journal, 3(3), 130–136.
Cite this article
-
APA : Zeb, A., Saeed, H. Y., & Khan, S. W. (2023). Impact of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus on the Severity of Coronary Artery Disease: Insights from Angiographic Assessment. Global Drug Design & Development Review, VIII(I), 28-34. https://doi.org/10.31703/gdddr.2023(VIII-I).05
-
CHICAGO : Zeb, Aurang, Hadi Yousaf Saeed, and Sher Wali Khan. 2023. "Impact of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus on the Severity of Coronary Artery Disease: Insights from Angiographic Assessment." Global Drug Design & Development Review, VIII (I): 28-34 doi: 10.31703/gdddr.2023(VIII-I).05
-
HARVARD : ZEB, A., SAEED, H. Y. & KHAN, S. W. 2023. Impact of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus on the Severity of Coronary Artery Disease: Insights from Angiographic Assessment. Global Drug Design & Development Review, VIII, 28-34.
-
MHRA : Zeb, Aurang, Hadi Yousaf Saeed, and Sher Wali Khan. 2023. "Impact of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus on the Severity of Coronary Artery Disease: Insights from Angiographic Assessment." Global Drug Design & Development Review, VIII: 28-34
-
MLA : Zeb, Aurang, Hadi Yousaf Saeed, and Sher Wali Khan. "Impact of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus on the Severity of Coronary Artery Disease: Insights from Angiographic Assessment." Global Drug Design & Development Review, VIII.I (2023): 28-34 Print.
-
OXFORD : Zeb, Aurang, Saeed, Hadi Yousaf, and Khan, Sher Wali (2023), "Impact of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus on the Severity of Coronary Artery Disease: Insights from Angiographic Assessment", Global Drug Design & Development Review, VIII (I), 28-34
-
TURABIAN : Zeb, Aurang, Hadi Yousaf Saeed, and Sher Wali Khan. "Impact of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus on the Severity of Coronary Artery Disease: Insights from Angiographic Assessment." Global Drug Design & Development Review VIII, no. I (2023): 28-34. https://doi.org/10.31703/gdddr.2023(VIII-I).05