01 Pages : 1-14
Abstract
Despite years of clinical research and trials of encouraging new therapies, cancer remains a leading cause of morbidity and mortality. The fragment-based drug discovery has evolved formerly as an efficient approach for identification, optimization, and generation of lead. After identifying the fragments having binding affinity with the target using computational method for fragment screening, they are optimized into more active compounds. This review elaborates the application of methodology of fragment-based drug design in designing potent and versatile anti-cancer drug candidates. It comprises of details such as construction of fragment library and screening, principles of library design, fragment hit identification, fragment to lead optimization, deconstruction and reconstruction approach, unified fragment based QSAR technique, phytochemical and pharmacophoric fragment based drug development and FBDD based targeting of epigenetic regulators in cancer. The agents discussed include STAT-3 inhibitor, vemurafenib, pazopanib, TAS-116 HSP-90 ?/? inhibitor, pexidartinib, venetoclax and erdafitinib, FBDD based designed Anticancer Agents.
Key Words
Fragment-Based Drug Design, Potent and Novel Anti-Cancer Agents, Fragment Optimization, Deconstruction-Reconstruction
Introduction
On the global scale, cancer is one of the main causes of human morbidity and mortality with 1.8 million new cancer cases diagnosed in 2020 and is correlated to the alterations or deletion of tumor suppressor genes (Siegel et al., 2020). The world is drawing close attention towards its clinical treatment. The amplification or mutation of oncogenes and enzyme/receptor inhibitors drives drug development process in breast, ovarian and colon cancer. Compared with biological and radiotherapy, chemotherapy is still the backbone of current scenario of the treatment (Li Q, 2020). Nonetheless, a broad range of these drugs is limited by a narrow therapeutic index, lethality, side-effects, suppression of immune system and acquired resistance by human body. Therefore, the expansion process of novel and versatile anticancer drugs with high efficiency, potency and less toxicity paved its way through fragment-based drug designing (FBDD) approach.
Development of new lead which specifically target cancerous cells and tumor is needed to overcome multidrug resistance which may be intrinsic or acquired. In the past years conventional technique of high-throughput screening (HTS) has played a significant role in the pharmaceutical industries with regard to drug design and discovery (Hassaan et al., 2020). However, in the present days fragment-based designing proved to be a substantial substitute to conventional methods of hit optimization and identification through the usage of the advantages of biochemical and biophysical methods for detecting small molecules or specific fragment binding to a specific enzyme along with the design of library of fragments which results in number of potent and versatile anti-neoplastic drugs or chemo reversal agents (Garner et al., 2019)
A major advantage in FBDD is that fragment hits with lower molecular weight compounds of range 120-300 Da as compared to HT screening campaign provides smooth starting points for drug leads generation. Moreover, the fraction of free binding affinity to the heavy atoms count i-e ligand efficiencies (LE) of larger ligands are usually smaller than for smaller ligands which results in the generation of lead compounds primed to possess improved physicochemical properties (Jacquemard & Kellenberger, 2019). To facilitate the optimization of fragment hits into potent molecules with drug-like characteristics, the three-dimensional mode of binding in the fragments is quantitatively determined using different techniques of X-ray crystallography or NMR spectroscopy. With the development of new approaches, FBDD played important roles in target-based drug discovery in cancer chemotherapy (Dang et al., 2017).
Fragment-based drug designing is widely employed in the pharmaceutical industry as an alternative method for hit identification and lead discovery as compared to traditional high-throughput screening approaches. It is increasingly employed in pharmaceutical industry for reducing attrition rates in all stages of drug processing and providing competent leads for biological targets which were previously intractable. Several drugs such as vemurafenib-an inhibitor of B-RAF kinase oncogenic activity derived from fragment-based approach is the first approved anti-cancer agents by FDA followed by erdafitinib and venetoclax which follows the mechanism of enzyme inhibition and results in treatment of brain tumor, cell lymphomas and various types of cancer. Hence, discovery of new anti-neoplastic agents through FBDD approach of identifying and optimizing fragment hits is the goal of current clinical trials so that they are applicable to diverse and specific targets to assess drug-ability, potency and efficacy in cancer treatment (Kidd et al., 2018).
Aims/Objectives
Our aim of study is directed to review the role of fragment-based drug discovery in designing potent agents used clinically in our battle against cancer. It is considered essential to share information with, and receive remarks from, clinical experts and health professionals especially when the methods are improvised for clinical development and are concluded. Efforts should be made to grow this collaboration and cooperation.
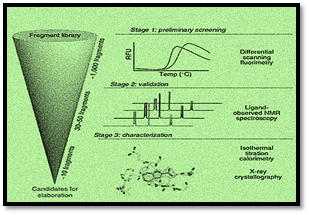
Construction of Fragment Library and Screening
In fragment-based approach, selection, construction, and screening of high-quality hits is essential for the development of resulting potent lead compound. Several biochemical and computational methods are employed for fragment screening and hit identification. Once identified, the fragments can be grown, merged, and linked to design versatile active compounds (Singh et al., 2018)
Principles of Library Design
In order to assemble fragment library for drug designing with high structural and chemical diversity, it is important to consider some primary criteria; (Kirsch et al., 2019).
1. Small compound library molecules, with molecular weight up to 300 Dalton comprising of diverse structural 500-1000 congeners are screened which serve as a starting point in fragment drug designing.
2. Fragments should follow the rule of three (RO3) with below mentioned drug-like properties
• The weight of the molecules should be ? 300 Da.
• The number of hydrogen bond donors should be ?3.
• The number of hydrogen bond acceptor should be ?3.
• The log P (Partition coefficient) value should be ?3.
3. Furthermore, the polar or the topological surface area of a fragment which is the sum of the surface of all the polar atoms of drug molecules with their attached hydrogen atoms should be ?60Ao with number of rotatable bonds ?3.
4. Fragment selectivity should be generated during the course of optimization.
Fragment Hit Identification and Screening
The main challenge in fragment-based drug designing is the selection
and detection of particular fragments which can bind to the target of interest.
Several orthogonal methods are employed for identification of promising
fragment, characterizing the mode of binding which includes biochemical and
biophysical techniques and to interrogate the ligand-target binding. Fragment
screening is more crucial step than high throughput screening (HTP), as the
ligand size is small which may result in lower binding affinities as well as
multi-target binding, leading to lower efficiency and potency of the fragment.
Table 1 displays the brief summary of biophysical screening methods employed in
fragment-based drug designing for evaluating the performance of fragments, size
of library of fragments and potency range of potential hits.
Table 1. Biophysical
screening methods for fragment screening (Zhong et al., 2019).
|
Screening Methods |
Description |
Size of Library |
Affinity Ranges in ?M |
|
Nuclear Magnetic
Resonance (NMR) |
NMR spectra (Two-dimensional) of proteins are examined either in the
presence or absence of fragments. Location of binding determined by chemical
shifts. |
1,000 compounds |
10–2,500 |
|
X-ray Crystallography |
Most dominant technique-applied for large proteins,
higher resolution. |
1,000–10,000compounds |
2–17,000 |
|
Biochemical Assays And Interferometry |
Binding and functional assays-Determines the refractive index and
thickness of protein layers. |
No limit |
0.1-100 |
|
Mass Spectrometry MS |
Determines the affinity, specificity and identify
different complexes- covalent and non-covalent interactions. |
Large dataset
|
0.1-100 |
Fragment to Lead Optimization
Various strategies are employed while performing the process of hit to
lead generation. Functional groups are attached to increase fragment size which
serves as a main objective for the installation of novel target-hit hot spots
to achieve a rational design fashion mainly known as growth vectors. For
enlargement, suitable analogues are generated for the identification of growth
factors. Three optimization strategies can help in the designing of a potent
and versatile lead for example in anti-cancer drug discovery. After
identification and screening of potential hits within the binding site of
protein they can be grown, merged, and linked on basis of various mechanisms.
Figure 1
Strategies of Fragment Optimization
Figure 1: Strategies of Fragment Optimization
Growing
Fragment growing is the common and straightforward method for optimization of fragments by obeying rule of three into a lead compound. Several chemical substituents are added for preferable interactions with the sub-pockets of the binding sites (Murray et al., 2019) The resulting compound is expected to have greater affinity with the target protein for example development of phosphodiesterase and kinase inhibitors are based on fragment growing approach in FBDD.
Linking
This attractive approach causes two or more than two fragments to bind to adjacent but different active sites of enzyme (Kang C., 2019). A linker moiety orients the individual fragments into a specific geometry providing maximum chances of binding affinity with the target. Fragment linking was performed in the discovery of non-peptide stromelysin inhibitors.
Merging
Multiple fragments which display multiple binding modes are combined by their key functional groups (Temple et al., 2019). Maintaining the mode of parent fragment is the limiting step in fragment merging which is mainly applied in the synthesis of Mycobacterium tuberculosisP450 CYP121 inhibitors.
Fragment based Drug Designing (FBDD) Approaches in Cancer Treatment
Phytochemical and Pharmacophoric Fragment Based Anticancer Drug Development
The main objective of phytochemical and pharmacophoric fragment based anticancer drug development is to design new anticancer leads that are capable of targeting cancer cells by using phytofragments that have been structurally screened. This technology has resulted in the lead compounds that may act as drug candidates showing less side effects and that may aid in the reduction of multidrug resistance (Rochlani et al., 2020).
Fragment Based QSAR Technique/ Computational Fragment Based Drug Design
The fragment based multi-target QSAR method/computational fragment-based drug design is employed to obtain the most appropriate fragments as structural alerts performing anti-cancer activity. This method is also used to develop innovative molecular entities that are expected, by this model, for being potentially potent and versatile anti-cancer agents (Eguida & Rognan, 2020). The methods most frequently used include.
Functional Group Counts
Functional group counts (FGC) act as descriptors and their role is to express specific fragment characteristics. They are number of certain functional moieties in any compound which are identified by the molecular compositional approaches and atomic connectivity.
Atom- Centered Fragments
Atom- centered fragments (ACF) are identified as quite useful descriptors providing useful information regarding hydrophobic and dispersive interactions linked to biological processes e.g. drug transport and distribution across the membrane. They are also capable of explaining the drug receptor interactions. ACF are the number of particular kinds of atoms in a certain molecule and can be identified by experimentally determining the molecular composition and atom connectivity.
Spectral Moments of the Bond Adjacency Matrix
For calculation of the spectral moments of the bond adjacency matrix a method called TOPS-MODE is used. TOPS-MODE stands for topological sub-structural molecular design. This approach has been used efficiently in describing certain physicochemical characteristics of organic compounds, employed in quantitative structure-toxicity relationship (QSTR) and also in shaping pharmacological activities (Kleandrova & Speck-Planche, 2020).
Targeting Epigenetic Regulators in Cancer by using Fragment-Based Drug Discovery
The development of cancer is closely linked with epigenetic changes like abnormal methylation of DNA and modifications of histone tail which cause depression of tumor suppressor gene, overexpression of oncogene and instable genome. These epigenetic points on the DNA pattern and histone proteins can be reversed which makes it possible to achieve the normal patterns (Alves Avelar et al., 2020). This can be done by targeting those epigenetic regulators chemically that are involved in generation, maintenance, recognition, and removal of these abnormal marks. Nowadays fragment based drug designing approach (FBDD) is being used for specifically targeting the protein-protein interactions (PPI) and the regulation of enzymes of epigenetic regulators. The fragments from compounds of less molecular weight (MW<300) are efficient in sampling chemical space and binding to specific target proteins e.g. the target proteins on the PPI interface (Murray & Rees, 2016). Hence recently a lot of research has been done in pharmaceutical companies and academic laboratories, aiming at the modification of epigenetic factors of oncogenes to design new and potent anti-cancer therapeutics (Feinberg et al., 2016).
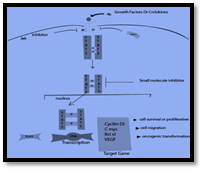
Fragment based Approach in Enzyme Inhibition
Enzymes are proteins catalyzing the biochemical reactions in living organisms. Sometimes, to stop or slow down the reaction a molecule is added known as eenzyme inhibitor. They are mostly used in pharmaceutical industry. The fragment-based approach has openend new ways to find the new small fragment molecules through testing to get the potent leading compound at the end. This fragment-based approach is used to find the anti-cancer agent in cancer therapy (Abell et al., 2020)
Phases of fragment-based approach
It comprises of four phases.
Target Enzymes Prepared
The suitable fragment to be selected should have certain properties e.g. it must be soluble and pure. However, to identify fragment used in fragment-based approach, different biophysical methods are used. For unliganded target protein, screening can be done with X- ray crystallography.
Build Fragment Libraries
Small molecules, having molecular mass less than 250Da, are used. However, molecules with weaker affinities give such solubility that screening of the substance can be done at millimolar concentration.
Screening of Fragments
These small fragments must bind with the target enzymes so first its necessary to identify different attributes of interaction. Bioassays usually don't give the required results so different biophysical techniques are used to get the results owing to weak affinity (Howard et al., 2020)
Develop Fragments into Prime Compounds
As directed in insilico approaches, development of fragment is done by the fragment binding intention and structural information is given by X-ray study to describe the leading compound (Ciulli, A. And Abell, C., 2020). Using different optimal active interactions, the potency of fragment molecules is built. Structural studies are performed using different techniques. At the end enzyme assays are conducted to check the potency.
Figure 2
Fragment based Approach in Enzyme Inhibition
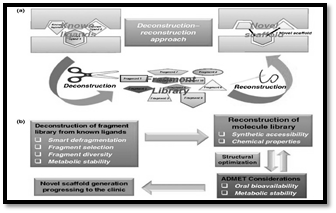
Deconstruction and Reconstruction Approach
This approach is diverse from FBS. It includes the deconstruction of ligands into comparatively littler part library. The deconstruction -remaking approach has developed as a valuable strategy. Fig (a) concurring to ponder on target proteins these parts did not rehash their location in a bigger ligand. The deconstructing part-based inhibitor is portrayed by utilizing the beta-lactamase which was partitioned into three parts that developed and separated indeed within the official design of their initial put with the first beta- lactamase complex. Yet numerous gotten parts did not involve their genuine authoritative locales in complex mechanism of different parts in protein- inhibitor complexes and did not guarantee the comparative authoritative mold (Chen et al., 2020). Parts inferred from the glycogen phosphorylase inhibitors, examined by Nuclear magnetic resonance technique, show the defragmentation which was not as it were to protect the official districts but propose cooperatives between authoritative locales. Think about of different deconstruction approaches recommend it as a convenient apparatus to investigate different protected nonpreserved authoritative locales. It’s done by examination of the peptide-protein complex through diverse X- beam crystallographics. So, deconstruction approach is utilized to construct a library of powerful parts from known ligands. Fig (b) builds a format of the authoritative locales and includes reproduction from the parts of library (Barelier et al., 2020). The reproduction approach includes numerous challenges compared to deconstruction of naturally dynamic sedate parts e.g. optimizing the parts by blending them to get sedate like properties whereas keeping up their authoritative modes. The remaking stage ought to be guided by classical approaches like Lipinski’s Run the show of Five and Veber’s Run the show. Subsequently we conclude that the deconstruction and remaking approach in FBDD is truly effective depending on open orgaic and chemical information.
Figure 3
Deconstruction-Reconstruction Approach (a) Schematic Representation (b) flow Diagram
Potent and Versatile Anti-Cancer Agents
Pexidartinib
Pexidartinib sold under brand name Turalio, is an orally administered and potent small molecule with selective inhibition activity against Colony-stimulating factor 1 receptor (CSF1R), which is a protein tyrosine kinase type III receptor and proto-oncogene receptor tyrosine kinase (KIT). In-silico enzyme inhibition fragment drug discovery approach is employed by screening 25,000 fragments in-house as source of prominent CSF1R inhibitors in synthesis of versatile anti-cancer agent Pexidartinib. Six diverse fragments (hits) were identified that exhibited affinity towards hinge regions of CSF1R (Benner et al., 2019).
Mechanism of Action
CSF1R molecular signaling pathway is essential for macrophage proliferation, differentiation, and survival in human body. High expression of CSFIR target receptors on the surface correlate and stimulate tumor progression process. Deviant expression of receptors serves to be an engaging target in treating different cancer types. The following mechanism is involved in the enzyme inhibition adopting fragment-based approach in Pexidartinib (Wesolowski et al., 2019).
Figure 4
Mechanism of action of
Clinical Use
• The FDA (USA) approved Pexidartinib in capsule dosage form in the treatment of symptomatic tenosynovial giant cell tumor (TGCT) in adults that is not likely to improve with surgery. TGCT was linked with severe morbidity with functional inabilities and mortality (Tap et al., 2019).
• Now-a-days, various malignancies are being investigated by using Pexidartinib as monotherapy or in combination therapy. Recent studies have shown that it casts the broadest network of clinical trials using monotherapy.
• CSF-1R inhibition in melanoma by Pexidartinib is used in the prostate cancer, glioblastoma (type of cancer that develops in astrocytes), classical Hodgkin lymphoma (production of abnormal B lymphocytes), neuro-fibroma (type of nerve tumor), sarcoma, and leukemia.
Vemurafenib
Zelboraf® (vemurafenib, PLX4032) is the first FDA approved drug developed using fragment-based approaches. The objective of the PLX4032 project was to discover selective RAF kinases inhibitors, specifically against the mutated oncogenic V600E. Initial screening of fragment indicated inhibition of other kinases but hid to lead study showed the desired selective inhibition of RAF- kinases. A fragment library consisting of 20000 scaffolds (with MW 150-350 Da) was selected and screening was done at a concentration of 200 µM in functional assays against specific kinases. Co-crystallography of initial hits was carried out. Hence fragments showing desired selective inhibition were identified. Zelboraf (PLX4032) was identified through fragment elaboration and selectivity was obtained during the process of lead optimization, which is a result of suitable fragment selection during FBDD (Erlanson et al., 2016).
Figure 5
Development of PLX4032
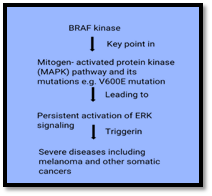
Mechanism of Action
Vemurafenib selectively inhibits the mutated BRAF V600E kinase hence leading to decrease in signaling through divergent mitogen activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway. Its efficacy is limited to 50% of observed melanomas involving BRAF V600E mutation (Torres-Collado et al., 2018).
Figure 6
Mechanism of Action
Clinical Use / Dosage
• Vemurafenib is clinically used in the treatment of metastatic melanoma along-with mutation in BRAF V600E that is unable to remove through surgery.
• ZELBORAF (vemurafenib) is available as tablets for oral administration. Each Zelboraf tablet contains 240 mg of vemurafenib.
• Vemurafenib is rapidly absorbed after a single dose of 960 mg given orally attaining maximum drug concentration after 4 hrs of administration. Extensive drug accumulation is achieved after multiple dosing at 960 mg given twice daily (Zhang et al., 2017).
Erdafitinib
Erdafitinib sold under the brand name Balversa, is the inhibitor of tyrosine kinase and fibroblast growth factor receptor (FGFR-1). It implies the usage of enzyme inhibition fragment derived drug discovery approach. The fragments have shown antitumor activity in drug delivery models and in a phase I study involving patients with FGFR alterations. Oral Erdafitinib is the first administered FDA approved inhibitor of fibroblast growth factor receptor (FGFR) kinase after successful completion of phase II clinical trials (Loriot et al., 2019).
Mechanism of Action
Fibroblast growth factor (FGF) signaling pathway play an important role from embryogenesis to wound healing in key biological processes and has strong connections to several hallmarks of cancer. FGF receptor (FGFR) genetic alterations lead to high rate of tumor growth, angiogenesis, metastasis, and low survival rate. The following mechanism is involved in the enzyme inhibition adopting fragment-based approach in Erdafitinib (Feng et al., 2020).
Figure 7
Mechanism of action of Erdafitinib
Clinical Use
• In the present review, recent knowledge of Erdafitinib clinical efficacy indicates the use in the treatment of localized metastatic or advanced Urothelial carcinoma (D’Angelo et al., 2020).
• The treatment is available for adult patients harboring genetic alterations in FGFR2/FGFR3 and is progressed within period of 12 months of an adjuvant or neo-adjuvant chemotherapy regimen. The therapy may include platinum or may be progressed after or prior to chemotherapy regimen in cancer treatment. 40% of patients responded to Erdafitinib therapy.
• Patients receiving Erdafitinib therapy are under strict therapeutic drug monitoring specifically for serum phosphate level elevations and vision changes.
Venetoclax
It is sold under brand name Venclexta and Venclyxto, is an oral selective BCL-2 inhibitor and antineoplastic agent for the use in malignancies. Library of small molecules were screened using protein-detected NMR spectroscopy. Fragment linking with a suitable acyl sulfonamide linker and parallel synthesis lead to development of versatile anti-cancer agent. It is a potent inhibitor of several anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 family including Bcl-xL, Bcl-2, and Bcl-w (Roberts et al., 2016).
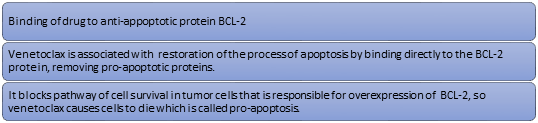
Mechanism of Action
Proteins of the Bcl-2 family are involved in apoptotic pathways. Venetoclax is a drug that enhances apoptosis which is a prominent way of cell death. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) cells are characterized by BCL-2 overexpression where it mediates tumor cell survival and has been associated with resistance to chemotherapies. The following mechanism is involved in the Bcl-2 inhibition adopting fragment-based approach in Venetoclax (Xi T. et al., 2018)
Figure 8
Mechanism of action of Venetoclax
Clinical Use
• Venetoclax is usually prescribed to the patients who have received at least one prior therapy with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) or small lymphocytic lymphoma (SLL) i-e patients with or without 17p deletion (Seymour et al., 2018).
• There may be TP53 mutation in adult patients who are not appropriate for or have malfunctioned B cell receptor pathway inhibition. Venclyxto monotherapy is indicated in chronic lymphocytic leukaemia (CLL), in adult patients who are not responding to both chemoimmunotherapy and a B cell receptor pathway inhibitor.
TAS-116 HSP-90?/? Inhibitor
FBDD engine has led to the discovery of TAS-116, which is a new HSP-90?/? inhibitor. TAS-116 binds to the standard binding sites as well as to the novel binding pocket thus showing a unique binding mode. Fragment designing is a unique methodology of drug designing which begins with screening step. Entirely sensitive screening techniques commonly biophysical methods are used as these fragments exhibit only low association with the potential target. High linking drug-like compounds are obtained through hit fragments by process of optimization based on cheminformatics and bioinformatics platforms (Doi et al., 2019).
Mechanism of Action
Heat shock protein 90 (HSP90) stabilizes the functioning of many client proteins including KIT (KIT Proto-Oncogene, Receptor Tyrosine Kinase) and EGFR (Aira et al., 2018). In cancer many of these functions are dysregulated. HSP90 inhibitor molecules completely block HSP90 enzymatic activity causing the degradation of client proteins. TAS-116 has high specificity for HSP-90?/? but does not inhibit other proteins of HSP-90 family like GRP94 present in endoplasmic reticulum and ribosomes or TRAP-I present in mitochondria. TAS-116 exhibited high efficiency in many heterograft models and comparatively it shows broad safety margins than the existing HSP-90 inhibitors (Obata et al., 2017).
Clinical Use
• The drug is an ATP- competitive and highly specific inhibitor of heat shock protein 90.
• Studies indicate the oral administration of TAS-116 allows more flexible dosage schedule than intravenous administration.
• The adverse reactions of TAS-116 are manageable as compared to other heat shock protein inhibitors.
• The drug exhibited significant activity in clinical trials irrespective of KIT primary and secondary alterations and also changes in PDGFRA.
• TAS-116 may be used a new treatment option for pretreated heavily gastrointestinal stromal tumor (Obata et al., 2018).
Pazopanib
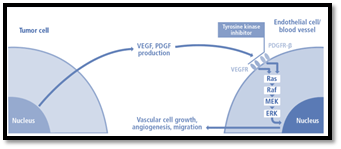
The fragment virtual screening based on the concept of Bayesian categorization is used for the designing of novel and potent scaffolds. The concept is applied on VEGFR-2 target. This model is effective for screening the compound databases as well as their respective fragment databases. Many fragments showed VEGFR-2 biological activity (Carles et al., 2018). FDA approved drug for clinical use, pazopanib which belongs to pyrimidines, was also discovered using this technique.
Mechanism of Action
Pazopanib (GW786034) is a novel inhibitor of tyrosine kinase. It exhibits antiangiogenic properties by inhibiting intracellular tyrosine kinase of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor and platelet derived growth factor receptor (Amr et al., 2018). Pazopanib targets VEGFR-1, -2, -3, PDGRF-? and -? and C-kit. The figure shows the role of pazopanib as an anticancer agent (Debnath et al., 2019).
Figure 9
Mechanism of action of Pazopanib
Clinical Use
• Pazopanib, sold under the brand name Votrient is an orally available angiogenesis inhibitor.
• Studies of Phase-I suggested the monotherapy dose of Pazopanib. Its recommended use is 800 mg once in a day.
• In 2009, the use of Pazopanib was approved in USA for the treatment of patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma (RCC).
• Pazopanib was approved in other countries and also showed clinically significant activity during Phase-II and Phase-III studies in patients having advanced soft tissue sarcoma (Boudou-Rouquette et al., 2016).
STAT-3 Inhibitor
Constitutive incitation of hail activator and regulator of translation 3 (STAT3) has been affirmed as an engaging pharmacological target in cancer treatment. To end both STAT3 incitation and dimer formation, a reasonable procedure is to arrange SH2 inhibitor space and phosphor-tyrosine authoritative area that is competent for both exercises. A modern fragment-based drug design (FBDD) method, in-silico examined site-directed FBDD, was used in corresponding study (Chen et al., 2020). Utilizing florescence polarization degree assay, a novel compound was identified to bind to STAT-3 SH2. However, till now FDA has not approved any drug targeting STAT-3. Therefore, the inquiry about more druggable STAT3 inhibitors with improved potency and bioavailability remains incredibly important (Yu, W, et al., 2020).
Figure 10
STAT-3 and the specific target sites for Inhibitors
Mechanism of Action
STAT- 3 inhibitor follows the following mechanism in cancer therapy (Gu, Y et al., 2020, Yue & Turkson, J., 2020).
Clinical Uses
• Inhibitor HJC0123 is a completely unique orally accessible STAT 3 inhibitor for breast and pancreatic advance apoptosis with range micromolar to nanomolar IC 50 values (Furqan et al., 2020).
• PY*LKTK-diminish harmful cell development
• SS610-decrease malignant cell development and increment apoptosis (Wong et al., 2020).
• S31- M2001-diminish harmful cell development, increment apoptosis, diminish movement.
Conclusion
Along with surgery, radiotherapy and stem cell transplant, effective chemotherapy is also considered a major treatment option for the chronic illness known as cancer. The drug resistance, acquired or intrinsic, is the major obstruction in way of efficient chemotherapy. Hence there is always a need to discover novel and efficient anti-cancer drugs or chemoreversal agents. The anti-cancer drug design has become very competitive as along with several prominent pharmaceutical industries, various biotechnological companies have also been working in this field. The fragment-based designing is proved to be an efficient approach in designing new drug-like molecules. Recently, there is a variety in number of reported drugs designing campaigns indicate promising results of this methodology in obtaining a final stable drug-likeness in molecule with high efficacy and potency as well as commendatory properties in a cost beneficial manner. Moreover, the application of this methodology may also provide the identification of structural properties therefore contributing to potential association to the target. This approach has been successful in launching many versatile anti-cancer agents such as STAT-3 inhibitor, vemurafenib, pazopanib, TAS-116, pexidartinib, venetoclax, erdafitinib etc. This useful approach is believed to have a bright future with elaborative applications in various drug designing platforms by pharmaceutical companies and academic research laboratories in the forthcoming years.
References
- Abell, C., Smith, A. and Blundell, T., (2020). Development of fragment-based approaches to build chemical tools for biology
- Aira, L. E., Villa, E., Colosetti, P., Gamas, P., Signetti, L., Obba, S., ... & Robert, G. (2018). The oncogenic tyrosine kinase Lyn impairs the pro-apoptotic function of Bim. Oncogene, 37(16), 2122-2136.
- Alves Avelar, L. A., Ruzic, D., Djokovic, N., Kurz, T., & Nikolic, K. (2020). Structure-based design of selective histone deacetylase 6 zinc binding groups. Journal of Biomolecular Structure and Dynamics, 38(11), 3166- 3177.
- Amr, A. E. G. E., Abo-Ghalia, M. H., Moustafa, G. O., Al-Omar, M. A., Nossier, E. S., & Elsayed, E. A. (2018). Design, synthesis, and docking studies of novel macrocyclic pentapeptides as anticancer multi-targeted kinase inhibitors. Molecules, 23(10), 2416
- Barelier, S., Pons, J., Marcillat, O., Lancelin, J. And Krimm, I., (2020). Fragment-Based Deconstruction of Bcl-Xl Inhibitors.doi.org/10.1021/jm100009z
- Benner, B., Good, L., Quiroga, D., Schultz, T. E., Kassem, M., Carson, W. E., ... & Wesolowski, R. (2020). Pexidartinib, a Novel Small Molecule CSF-1R Inhibitor in Use for Tenosynovial Giant Cell Tumor: A Systematic Review of Pre-Clinical and Clinical Development. Drug Design, Development and Therapy, 14, 1693.
- Boudou-Rouquette, P., Tlemsani, C., Blanchet, B., Huillard, O., Jouinot, A., Arrondeau, J., ... & Goldwasser, F. (2016). Clinical pharmacology, drug-drug interactions, and safety of pazopanib: a review. Expert Opinion on Drug Metabolism & Toxicology, 12(12), 1433-1444.
- Carles, F., Bourg, S., Meyer, C., & Bonnet, P. (2018). PKIDB: A curated, annotated, and updated database of protein kinase inhibitors in clinical trials. Molecules, 23(4), 908
- Chen, H., Yang, Z., Ding, C., Chu, L., Zhang, Y., Terry, K., Liu, H., Shen, Q. And Zhou, J., (2020). Fragment-Based Drug Design and Identification of HJC0123, A Novel Orally Bioavailable STAT3 Inhibitor for Cancer Therapy
- Chen, H., Zhou, X., Wang, A., Zheng, Y., Gao, Y. And Zhou, J., (2020). Evolutions in Fragment- Based Drug Design: The Deconstruction- Reconstruction Approach.
- Ciulli, A. And Abell, C., (2020). Fragment-Based Approaches to Enzyme Inhibition.
- D'Angelo, A., Bagby, S., Galli, I. C., Bortoletti, C., & Roviello, G. (2020). Overview of the clinical use of erdafitinib as a treatment option for the metastatic urothelial carcinoma: where do we stand. Expert Review of Clinical Pharmacology, 1-8.
- Dang, C. V., Reddy, E. P., Shokat, K. M., & Soucek, L. (2017). Drugging the'undruggable'cancer targets. Nature Reviews Cancer, 17(8), 502
- Debnath, S., Kanakaraju, M., Islam, M., Yeeravalli, R., Sen, D., & Das, A. (2019). In silico design, synthesis, and activity of potential drug-like chrysin scaffold-derived selective EGFR inhibitors as anticancer agents. Computational Biology and Chemistry, 83, 107156.
- Doi, T., Kurokawa, Y., Sawaki, A., Komatsu, Y., Ozaka, M., Takahashi, T., ... & Nishida, T. (2019). Efficacy and safety of TAS-116, an oral inhibitor of heat shock protein 90, in patients with metastatic or unresectable gastrointestinal stromal tumour refractory to imatinib, sunitinib and regorafenib: a phase II, single-arm trial. European Journal of Cancer, 121, 29-39.
- Eguida, M., & Rognan, D. (2020). A computer vision approach to align and compare protein cavities: Application to fragment-based drug design. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry.
- Erlanson, D. A., Fesik, S. W., Hubbard, R. E., Jahnke, W., & Jhoti, H. (2016). Twenty years on: the impact of fragments on drug discovery. Nature reviews Drug discovery, 15(9), 605.
- Feinberg, A. P., Koldobskiy, M. A., & Göndör, A. (2016). Epigenetic modulators, modifiers, and mediators in cancer aetiology and progression. Nature Reviews Genetics, 17(5), 284-299.
- Feng, W., Zhang, M., Wu, Z. X., Wang, J. Q., Dong, X. D., Yang, Y., ... & Yang, D. H. (2020). Erdafitinib antagonizes ABCB1-mediated multidrug resistance in cancer cells. Frontiers in Oncology, 10.
- Furqan, M., Akinleye, A., Mukhi, N., Mittal, V., Chen, Y. And Liu, D., (2020). STAT Inhibitors for Cancer Therapy
- Garner, P., Cox, P. B., Rathnayake, U., Holloran, N., & Erdman, P. (2019). Design and Synthesis of Pyrrolidine-based Fragments That Sample Three-dimensional Molecular Space. ACS Medicinal Chemistry Letters, 10(5), 811- 815.
- Gu, Y., Mohammad, I. And Liu, Z., (2020). Overview of the STAT-3 Signalling Pathway in Cancer and The Development of Specific Inhibitors (Review)
- Hassaan, E., Hohn, C., Ehrmann, F. R., Goetzke, F. W., Movsisyan, L., Hüfner-Wulsdorf, T., ... & Klebe, G. (2020). Fragment Screening Hit Draws Attention to a Novel Transient Pocket Adjacent to the Recognition Site of the tRNA-Modifying Enzyme TGT. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry.
- Howard, N., Abell, C., Blackmore, W., Chessari, G., Congreve, M., Howard, S., Jhoti, H., W. Murray, C., Seavers, L. And Montfort, R., (2020). Application of Fragment Screening and Fragment Linking to The Discovery of Novel Thrombin Inhibitors,
- Jacquemard, C., and Kellenberger, E., (2019). A bright future for fragment-based drug discovery: what does it hold? Exp. Opin. Drug Discov. 14, 413-416. doi: 10.1080/17460441.2019.1583643
- Kang, C. B. (2019) F-NMR in target-based drug discovery. Curr. Med. Chem. 26, 4964- 4983. doi: 10.2174/0929867326666190610160534.
- Kidd, S. L., Osberger, T. J., Mateu, N., Sore, H. F., & Spring, D. R. (2018). Recent applications of diversity-oriented synthesis toward novel, 3-dimensional fragment collections. Frontiers in chemistry, 6, 460.
- Kirsch, P., Hartman, A. M., Hirsch, A. K., & Empting, M. (2019). Concepts and core principles of fragment-based drug design. Molecules, 24(23), 4309.
- Kleandrova, V. V., & Speck-Planche, A. (2020). The QSAR paradigm in fragment-based drug discovery: from the virtual generation of target inhibitors to multi-scale modeling. Mini reviews in medicinal chemistry, 20(14), 1357-1374.
- Li Q (2020) Application of Fragment-Based Drug Discovery to Versatile Targets. Front. Mol. Biosci. 7:180. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2020.00180
- Loriot, Y., Necchi, A., Park, S. H., Garcia-Donas, J., Huddart, R., Burgess, E., ... & Joshi, M. (2019). Erdafitinib in locally advanced or metastatic urothelial carcinoma. New England Journal of Medicine, 381(4), 338- 348
- Murray, C. W., & Rees, D. C. (2016). Opportunity knocks: organic chemistry for fragment- based drug discovery (FBDD). Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 55(2), 488- 492.
- Murray, C. W., Newell, D. R., & Angibaud, P. (2019). A successful collaboration between academia, biotech and pharma led to discovery of erdafitinib, a selective FGFR inhibitor recently approved by the FDA. MedChemComm, 10(9), 1509-1511.
- Obata, Y., Horikawa, K., Shiina, I., Takahashi, T., Murata, T., Tasaki, Y., ... & Abe, R. (2018). Oncogenic Kit signalling on the Golgi is suppressed by blocking secretory trafficking with M-COPA in gastrointestinal stromal tumours. Cancer Letters, 415, 1- 10.
- Obata, Y., Horikawa, K., Takahashi, T., Akieda, Y., Tsujimoto, M., Fletcher, J. A., ... & Abe, R. (2017). Oncogenic signaling by Kit tyrosine kinase occurs selectively on the Golgi apparatus in gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Oncogene, 36(26), 3661-3672.
- Roberts, A. W., Davids, M. S., Pagel, J. M., Kahl, B. S., Puvvada, S. D., Gerecitano, J. F., ... & Wong, S. (2016). Targeting BCL2 with venetoclax in relapsed chronic lymphocytic leukemia. New England Journal of Medicine, 374(4), 311-322.
- Rochlani, S. P., Choudhari, P. B., & Dahiwade, L. K. (2020). Phytochemical and Pharmacophoric Fragment Based Anticancer Drug Development. Current computer-aided drug design
- Saito, Y., Takahashi, T., Obata, Y., Nishida, T., Ohkubo, S., Nakagawa, F., ... & Sugase, T. (2020). TAS-116 inhibits oncogenic KIT signalling on the Golgi in both imatinib-naïve and imatinib-resistant gastrointestinal stromal tumours. British journal of cancer, 122(5), 658-667.
- Seymour, J. F., Kipps, T. J., Eichhorst, B., Hillmen, P., D'Rozario, J., Assouline, S., ... & Jaeger, U. (2018). Venetoclax-rituximab in relapsed or refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia. New England Journal of Medicine, 378(12), 1107-1120
- Siegel, R. L., Miller, K. D., & Jemal, A. (2020). Cancer statistics, 2020. CA: a cancer journal for clinicians, 70(1), 7-30.
- Wong, A., Hirpara, J., Pervaiz, S., Eu, J., Sethi, G. And Goh, B., (2020). Do STAT3 Inhibitors Have Potential in the Future for Cancer Therapy?
- Singh, M., Tam, B., & Akabayov, B. (2018). NMR- fragment based virtual screening: A brief overview. Molecules, 23(2), 233.
- Xi, T., Qingli, T., Fengrui, L., & Fengxiang, T. (2018). Advances in the Synthesis of Venetoclax as a New Drug for the Treatment of Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. Chemistry, (2), 3.
- Tap, W. D., Gelderblom, H., Palmerini, E., Desai, J., Bauer, S., Blay, J. Y., ... & Thomas, D. M. (2019). Pexidartinib versus placebo for advanced tenosynovial giant cell tumour (ENLIVEN): a randomised phase 3 trial. The Lancet, 394(10197), 478-487.
- Yu, W., Xiao, H., Lin, J. And Li, C., 2020. Discovery of Novel STAT3 Small Molecule Inhibitors Via In Silico Site-Directed Fragment-Based Drug Design.J Med Chem.
- Temple, K. J., Engers, J. L., Long, M. F., Gregro, A. R., Watson, K. J., Chang, S., ... & Bridges, T. M. (2019). Discovery of a novel 3, 4- dimethylcinnoline carboxamide M4 positive allosteric modulator (PAM) chemotype via scaffold hopping. Bioorganic & medicinal chemistry letters, 29(21), 126678
- Yue, P. And Turkson, J., 2020. Targeting STAT3 In Cancer: How Successful Are We?
- Torres-Collado, A. X., Knott, J., & Jazirehi, A. R. (2018). Reversal of resistance in targeted therapy of metastatic melanoma: lessons learned from vemurafenib (BRAFV600E-Specific Inhibitor). Cancers, 10(6), 157
- Zhang, W., Heinzmann, D., & Grippo, J. F. (2017). Clinical pharmacokinetics of vemurafenib. Clinical Pharmacokinetics, 56(9), 1033- 1043.
- Zhong, W., Koay, A., Ngo, A., Li, Y., Nah, Q., Wong, Y. H., ... & Foo, K. (2019). Targeting the bacterial epitranscriptome for antibiotic development: Discovery of novel tRNA- (N1G37) methyltransferase (TrmD) inhibitors. ACS infectious diseases, 5(3), 326-335.
- Wesolowski, R., Sharma, N., Reebel, L., Rodal, M. B., Peck, A., West, B. L., ... & Le, M. H. (2019). Phase Ib study of the combination of pexidartinib (PLX3397), a CSF-1R inhibitor, and paclitaxel in patients with advanced solid tumors. Therapeutic advances in medical oncology, 11, 1758835919854238.
Cite this article
-
APA : Zahra, S. A., Imran, A., & Khalid, F. (2020). Fragment-Based Approach towards the Design of Potent and Versatile Anti-Cancer Agents. Global Drug Design & Development Review, V(I), 1-14. https://doi.org/10.31703/gdddr.2020(V-I).01
-
CHICAGO : Zahra, Sana Ali, Ayesha Imran, and Faiza Khalid. 2020. "Fragment-Based Approach towards the Design of Potent and Versatile Anti-Cancer Agents." Global Drug Design & Development Review, V (I): 1-14 doi: 10.31703/gdddr.2020(V-I).01
-
HARVARD : ZAHRA, S. A., IMRAN, A. & KHALID, F. 2020. Fragment-Based Approach towards the Design of Potent and Versatile Anti-Cancer Agents. Global Drug Design & Development Review, V, 1-14.
-
MHRA : Zahra, Sana Ali, Ayesha Imran, and Faiza Khalid. 2020. "Fragment-Based Approach towards the Design of Potent and Versatile Anti-Cancer Agents." Global Drug Design & Development Review, V: 1-14
-
MLA : Zahra, Sana Ali, Ayesha Imran, and Faiza Khalid. "Fragment-Based Approach towards the Design of Potent and Versatile Anti-Cancer Agents." Global Drug Design & Development Review, V.I (2020): 1-14 Print.
-
OXFORD : Zahra, Sana Ali, Imran, Ayesha, and Khalid, Faiza (2020), "Fragment-Based Approach towards the Design of Potent and Versatile Anti-Cancer Agents", Global Drug Design & Development Review, V (I), 1-14
-
TURABIAN : Zahra, Sana Ali, Ayesha Imran, and Faiza Khalid. "Fragment-Based Approach towards the Design of Potent and Versatile Anti-Cancer Agents." Global Drug Design & Development Review V, no. I (2020): 1-14. https://doi.org/10.31703/gdddr.2020(V-I).01