Abstract
This retrospective research examined 150 people five years after their initial cerebral fluid shunt. Hydrocephalus aetiology, infection rates, and shunt age were investigated. Medical records were evaluated for hydrocephalus aetiology, surgical evaluations of under-one-year-olds, infection rates, and treatments. Statistics examined hydrocephalus aetiology, infection rate, and age. Meningomyelocele was 40%, obstructed or congenital communication 33%, tumours 18%, and meningitis or intraventricular haemorrhage the remainder. 83% of surgeries were on under-12-month-olds, 18% on newborns. 33 infections resulted from 22% per person and 6% each surgery. Seniors had lower infection rates (P < 0.01) than meningomyelocele patients (P=0.06). Meningomyelocele and congenital hydrocephalus patients require age-related infection studies. Shunting after two weeks may reduce meningomyelocele infection rates.
Key Words
Hydrocephalus, Cerebral Fluid Shunt, Retrospective Analysis, Aetiology, Infection Rate, Age at Shunt Placement, Meningomyelocele, Acetazolamide, Furosemide
Introduction
Hydrocephalus, characterized by the abnormal accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid within the brain, is a complex neurological condition that requires appropriate management to prevent severe complications. Cerebral fluid shunt placement has emerged as a common and effective treatment approach for hydrocephalus, diverting the excess fluid and alleviating intracranial pressure (Kulkarni et al., 2010). However, various factors, including the cause of hydrocephalus, infection rates, and the age at which shunt placement occurs, may influence the outcomes and complications associated with this procedure. The surgical procedure of CSF placement: an otherwise successful operation of neurosurgery, can be converted into a nightmare for the patient undergoing surgery because it can cause infections; a very serious risk factor of it, with long-lasting effects on the development and survival rate of a child and on the cost and duration of hospitalization (Zhou et al., 2022).
The rate of infection in shunted children with hydrocephalus, which ranges between 7% and 30%, is still higher, in spite of attempting many efforts, including the use of surgical isolators and prophylactic antibiotics. A roughly 20% infection rate has been sought out in some series (Gholampour et al., 2023). Hydrocephalus aetiology and the age of the patient at the time of shunt insertion are the two major risk factors which can cause infections from shunt placement and thus these two have taken a lot of attention in the published literature and have shown their importance in the shunt infection's development. This retrospective research study aims to investigate the association between the cause of hydrocephalus, infection rates, and the age at shunt placement in a cohort of 150 individuals who underwent their first cerebral fluid shunt placement approximately ten years ago. Understanding the relationships between these factors is crucial for optimizing treatment strategies and improving patient outcomes (Teping et al., 2023).
The distribution of hydrocephalus etiologies will be thoroughly examined, including the prevalence of conditions such as meningomyelocele, non-communicating hydrocephalus, obstructive hydrocephalus or congenital communicating, tumours, meningitis, intraventricular haemorrhage, and other related conditions. By analyzing the medical records of the participants, valuable insights can be gained into the diversity of underlying causes contributing to hydrocephalus development (Kulkarni et al., 2011). Furthermore, the age distribution at the period of bypass placement was carefully evaluated, with a particular focus on cases occurring in infants under one year of age and those as young as one week old (Naik et al., 2022). This analysis shed light on the potential influence of age on infection rates and overall treatment outcomes. In addition, the total number of treatments and infection rates per individual and per surgery were assessed to assess the impact of these factors on the overall infection risk.
Statistical analysis was performed to identify any significant associations between the cause of hydrocephalus, infection rates, and the age at shunt placement (Gholampour et al., 2022). The results of this investigation might improve our comprehension of the underlying causes, contributing to infection susceptibility and guide clinical decision-making in terms of optimal timing for shunt placement (Panagopoulos et al., 2022). Ultimately, this research aims to provide valuable insights into the complex interplay between hydrocephalus aetiology, infection rates, and age at shunt placement. The outcomes of this study have the potential to inform clinical practices, improve treatment protocols, and optimize patient outcomes in individuals with hydrocephalus (Liu et al., 2022).
Methodology
Study Design and Setting
The Khyber Teaching Hospital hosted this research from January 2022 through January 2023. The research comprised 150 kids who had shunt implantation in total.
Participant Characteristics
With a median age of six weeks and varying in age from a single day to sixteen years, the study's patients had a median age of 1.4 years. Four groups were established according to the patients' ages at the point of surgery: Patients in Group 1 were aged one week or less (18%, n=27), those in Group 2 were in the range of two and eight weeks (40%, n=60), those in Group 3 were among nine and 52 weeks (25%, n=37), and those in Group 4 were above fifty-two weeks (45%, n=60) and Group 4 included patients older than fifty-two weeks (17%, n=26). The distribution of hydrocephalus etiologies in the patient population was as follows: meningomyelocele and constrictive hydrocephalus (40%), obstructive hydrocephalus or congenital communicating (33%), tumours (18%), meningitis, and intraventricular haemorrhage (8%).
Shunt Procedure and Follow-up
Ventriculoperitoneal (VP) shunt placement was the predominant procedure used, utilizing the chabbra ventriculoperitoneal Shunt equipment. Out of the total 150 patients, 129 had accurate follow-up data available. Patients who developed shunt infections had their shunts removed upon evident signs of infection, while those without infections had their follow-up terminated two years post-operation. Nineteen cases had incomplete follow-up data, with 26% having meningomyelocele, 32% having tumours, and 42% having communicating hydrocephalus.
Identification of Shunt Infections
Shunt infections were identified based on positive results from gram stain or shunt culture, or when symptoms such as induration, pyogenic fluid, and erythema were observed in the shunt area. Perioperative antibiotic usage varied during the study period.
Statistical Analysis
The chi-square test was utilized for statistical analysis.
Study Limitations
This study focused solely on analyzing shunt infections in children with hydrocephalus, and no data regarding intellectual outcomes, mortality, or long-term consequences were included in the analysis.
Methodology
Study Design and Setting
The Khyber Teaching Hospital hosted this research from January 2022 through January 2023. The research comprised 150 kids who had shunt implantation in total.
Participant Characteristics
With a median age of six weeks and varying in age from a single day to sixteen years, the study's patients had a median age of 1.4 years. Four groups were established according to the patients' ages at the point of surgery: Patients in Group 1 were aged one week or less (18%, n=27), those in Group 2 were in the range of two and eight weeks (40%, n=60), those in Group 3 were among nine and 52 weeks (25%, n=37), and those in Group 4 were above fifty-two weeks (45%, n=60) and Group 4 included patients older than fifty-two weeks (17%, n=26). The distribution of hydrocephalus etiologies in the patient population was as follows: meningomyelocele and constrictive hydrocephalus (40%), obstructive hydrocephalus or congenital communicating (33%), tumours (18%), meningitis, and intraventricular haemorrhage (8%).
Shunt Procedure and Follow-up
Ventriculoperitoneal (VP) shunt placement was the predominant procedure used, utilizing the chabbra ventriculoperitoneal Shunt equipment. Out of the total 150 patients, 129 had accurate follow-up data available. Patients who developed shunt infections had their shunts removed upon evident signs of infection, while those without infections had their follow-up terminated two years post-operation. Nineteen cases had incomplete follow-up data, with 26% having meningomyelocele, 32% having tumours, and 42% having communicating hydrocephalus.
Identification of Shunt Infections
Shunt infections were identified based on positive results from gram stain or shunt culture, or when symptoms such as induration, pyogenic fluid, and erythema were observed in the shunt area. Perioperative antibiotic usage varied during the study period.
Statistical Analysis
The chi-square test was utilized for statistical analysis.
Study Limitations
This study focused solely on analyzing shunt infections in children with hydrocephalus, and no data regarding intellectual outcomes, mortality, or long-term consequences were included in the analysis.
Results
In
total, with an average of three treatments per individual, 455 treatments were
completed. The rate of infection per individual was 22% and per surgery was 6%,
of total 33 patients presented with infections. Although the patients diseased
with meningomyelocele appeared to be more susceptible to infection than those
who were having congenital hydrocephalus (P= 0.06), still no remarkable
association was apparent between the infection rate and the cause of the
hydrocephalus (P > 0.05). Almost all the patients with congenital
hydrocephalus and meningomyelocele (94% and 98.2%, respectively) were
discharged early, but most of the patients (78%) with tumours were discharged
late. Age was a factor in the rate of infection at the moment the shunt was
implanted, i.e., older patients were less prone to contaminations than younger
ones (P < 0.01). Patients aged between two to eight weeks seem to have an
intermediate condition.
Table 1 provides a summary of participant
characteristics and infection rates in the study. Based on the patients' ages
at the time of surgery, four categories of age were created: Group 1 (1 week),
the second group (2-8 weeks), the third group (9-52 weeks), & Group 4 (>
52 weeks). The distribution of hydrocephalus etiologies among each age group
and the total amount of individuals suffering from it in each age category are
also included in the table.
The
infection rates per individual and per surgery are presented in the table. The
overall infection rate per individual was 22%, indicating that 22% of the total
participants experienced shunt infections at some point. The infection rate per
surgery was 6%, indicating that 6% of the total number of shunt surgeries
resulted in infections.
Table 1
Participant Characteristics
and Infection Rates
|
Age Group |
Age Range |
Number of Patients |
Hydrocephalus Etiologies |
Infection Rate (Per
Individual) |
Infection Rate (Per
Surgery) |
|
Group
1 |
? 1 week |
27 |
Meningomyelocele (26%),
Tumors (32%), Constrictive Hydrocephalus (42%) |
- |
- |
|
Group
2 |
2-8 weeks |
60 |
- |
- |
- |
|
Group
3 |
9-52 weeks |
37 |
- |
- |
- |
|
Group
4 |
> 52 weeks |
26 |
- |
- |
- |
|
Total |
- |
150 |
- |
22% |
6% |
Due to fewer cases in all age categories
(meningitis, IVH) or an uneven distribution (seventy eight% of tumours were
diagnosed in the second year of life), the association of aetiology with the
rate of infection in the tumour, age, IVH, meningitis, or hydrocephalus
patients could not be established throughout the duration of shunt positioning.
Due to the considerable proportion of patients in all categories who were
transferred throughout all of the time periods (less than 1 week, 2 to 8 weeks,
and 9 to 52 weeks) during the span of a year, such connections were made
feasible for the congenital hydrocephalus and meningomyelocele patients (figure
1).
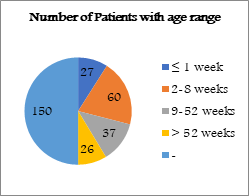
Figure 1
Figure 1: showing the number of patients with age 48% of the meningomyelocele patients, who were shunted during the first week after birth, were infected, in comparison to 24% of those who were shunted in 2 to 8 weeks and 16% of those who were shunted in 9 to 51 weeks of age (P=0.01). The rate of infection had not significantly changed in meningomyelocele patients who were discharged within 2 to 8 weeks of duration (P > 0.05). There was no remarkable variation in the rate of infection among congenital hydrocephalus patients who were shunted at the first week, 2 to 9 weeks to 51 weeks of age (P > 0.05).
Discussion
To emphasize the significance of preventing shunt infection from occurring, it is important to explain the negative results and influence on the lives and growth of the kid. It is generally accepted that the shunt device was contaminated surgically and afterwards colonized can lead to infection. Surgical isolators or perioperative antibiotics have failed to successfully lower the prevalence of this colonization (Elbaroody et al., 2023). In reality, recent data indicate a 15% to 20% infection incidence per patient. To lessen the prevalence of shunt infection in children, a fuller knowledge of the variables related to shunt illnesses and their subsequent management, where feasible, might be very helpful. Our infection rate, at 22% per patient, is similar to that described in the scientific literature, and the demographics of our patients—their ages and the causes of their hydrocephalus—represent those of a neurosurgery department in an important children's hospital. According to the patient's age, four subcategories were chosen according to clinical knowledge to differentiate between extremely early, early, late, & very late shunt insertion (Vrettou et al., 2022). The first two categories correspond to the birth and very young infant stages, the third to infancy, and the final one to the adolescent stage.
We hypothesize that there is a relationship between the frequency of infection and the aetiology of hydrocephalus, and the resultant P-value (P = 0.06) is approaching significance (limited to a comparison between MM and CH). Currently, possibly one cannot say yet whether this is a trend. However, comparing the infection rates in the CH and MM groups (Dewan et al., 2023), which, in all of the three seasons of the year, were the only two categories with a tolerable amount of patients transferred, clearly points to a highly grey region. Our results suggest that the meningomyelocele patients had a higher rate of infection agreed, with earlier research. With the other patient groups, we didn't perform bilateral analysis, Due to the small patient populations in the M and IVH groups as well as the unbalanced "distribution of the T patients", 78% of which had been moved beyond fifty-two weeks of age (Verhey et al., 2023), the M and IVH groups had a restricted number of patients. It seems that the infection rate & age at the period of shunt placement are correlated since younger patients had a higher infection rate than older patients. Due to the reason that based on the etiological group it varies (Bastian et al., 2022), it should be carefully comprehended. It is still true in the meningomyelocele group but is uncertain in the congenital hydrocephalus group. There are different studies associating the age of shunted children with hydrocephalus and the rate of infections in the literature. However, none of these analyses how this relation acts in the different etiological groupings. Due to the manageable proportion of CH as well as MM individuals that were moved across all three time zones, we were in a position to analyze this (Elbaroody et al., 2023).
Medication as a treatment for hydrocephalus is controversial. It should be used only as a temporary measure for posthemorrhagic hydrocephalus in neonates, or when shunting is not possible. Our result shows that meningomyelocele patients after shunting within the first week after birth were having a very high rate of infection is not unexpected. In fact, "a meningomyelocele can be thought of as a clean-contaminated or contaminated wound" (Kitamura et al., 2021). "The insertion of a foreign body (shunt) in close temporal proximity to the closure of the contaminated wound (meningomyelocele repair) may increase the incidence of shunt infections. Meningomyelocele, however, may be thought of as a clean-contaminated or infected wound, and the insertion of a foreign substance (shunt) in close temporal proximity to the healing of the infected wound (MM repair) may increase the probability of shunt infections" (Reeves et al., 2020).
Conclusions
The infection rate of CSF shunts is a complex issue influenced by various factors, including hydrocephalus causes and the Age of the patient when the shunt was implanted. Matching patient groups in terms of age and hydrocephalus etiology is crucial when comparing infection rates across different studies. Our analysis focused on congenital hydrocephalus (CH) and meningomyelocele (MM) patients, as they were well-classified within the first year of life. Based on our findings, we draw the following conclusions:
a. The hydrocephalus cause does not significantly impact the infection rate, Despite a trend (P=0.06) that suggests “MM patients” may have a greater infection incidence than CH patients. This conclusion needs more supporting data.
b. If "MM patients" are shunted during the initial week of life, their infection incidence is significantly greater than if they are shunted at a minimum of two weeks later (P 0.01). The same trend is observed for CH patients (P=0.05). Therefore, it may be beneficial to delay shunt placement until at least two weeks of life in these patient groups, as early shunt insertion throughout the initial week is connected to a 48% rise in infection rate. Surgery for CSF shunt placement should be postponed unless there is a significant threat to the patient's life due to rising intracranial pressure.
References
- Bastian, R. A., Pramusinto, H., Basuki, E., & Marianne, M. (2022). Ventriculoperitoneal Shunt Infection: A Study about Age as a Risk Factor in Hydrocephalus Pediatrics. Open Access Macedonian Journal of Medical Sciences, 10(B), 314–319.
- Dewan, M. C., Isaacs, A. M., Cools, M. J., Yengo- Kahn, A., Naftel, R. P., Jensen, H., ... & Wellons III, J. C. (2023). Treatment of hydrocephalus following posterior fossa tumor resection: a multicenter collaboration from the Hydrocephalus Clinical Research Network. Journal of Neuro-Oncology, 1-10. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-023-04316-4
- Elbaroody, M., Ezz, A., Eldessouky, A. H., Hassan, A. A. A. N., Elsharkawy, A. A., Ali, K. B., & El Refaee, E. A. (2023). Is It Possible to Eliminate Postoperative Shunt Infections?: Results of a Modified Hydrocephalus Clinical Research Network Protocol. Journal of Neurological Surgery Part A: Central European Neurosurgery.
- Gholampour, S., Nguyen, A., & Chaudry, S. (2023). Intracranial compliance, resistance to CSF-outflow, and pressure-volume index in hydrocephalus patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. IRBM, 100785.
- Gholampour, S., Patel, J., Yamini, B., & Frim, D. (2022). Cerebrospinal fluid hydrocephalus shunting: cisterna magna, ventricular frontal, ventricular occipital. Neurosurgical Review, 45(4), 2615-2638.
- Kitamura, F. C., Pan, I., Ferraciolli, S. F., Yeom, K. W., & Abdala, N. (2021). Clinical artificial intelligence applications in radiology: neuro. Radiologic Clinics, 59(6), 1003-1012.
- Kulkarni, A. V. (2011). Erratum: Predicting who will benefit from endoscopic third ventriculostomy compared with shunt insertion in childhood hydrocephalus using the ETV Success Score. Journal of Neurosurgery: Pediatrics, 7(2), 221-221.
- Kulkarni, A. V., Drake, J. M., Kestle, J. R., Mallucci, C. L., Sgouros, S., & Constantini, S. (2010). Predicting who will benefit from endoscopic third ventriculostomy compared with shunt insertion in childhood hydrocephalus using the ETV Success Score. Journal of Neurosurgery: Pediatrics, 6(4), 310-315.
- Liu, G., & Nie, C. (2022). Ultrasonic Diagnosis and Management of Posthemorrhagic Ventricular Dilatation in Premature Infants: A Narrative Review. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(24), 7468.
- Naik, A., Ramsy, N., Krist, D. T., Taha, B., Dharnipragada, R., Khanam, R., ... & Arnold, P. M. (2022). Anterior vs. Posterior Ventricular Catheter Placement in Pediatric Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta- Analysis. World neurosurgery. h
- Panagopoulos, D., Strantzalis, G., Gavra, M., Boviatsis, E., & Korfias, S. (2022). The Role of Antisiphon Devices in the Prevention of Central Ventricular Catheter Obliteration for Hydrocephalus: A 15-Years Institution’s Experience Retrospective Analysis. Children, 9(4), 493.
- Reeves, B. C., Karimy, J. K., Kundishora, A. J., Mestre, H., Cerci, H. M., Matouk, C., ... & Kahle, K. T. (2020). Glymphatic system impairment in Alzheimer’s disease and idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus. Trends in Molecular Medicine, 26(3), 285-295.
- Teping, F., Huelser, M., Sippl, C., Zemlin, M., & Oertel, J. (2023). From fixed-pressure paediGAV to programmable proGAV/proSA serial valves for pediatric hydrocephalus within the 1st year of life: a technical single-center analysis. Journal of Neurosurgery: Pediatrics, 31(6), 536-544.
- Verhey, L. H., Maharaj, A., Patel, N., Manoranjan, B., Ajani, O., Fleming, A., ... & Pediatric Brain Tumor Study Group. (2023). External ventricular drainage in the management of pediatric patients with posterior fossa tumors and hydrocephalus: a retrospective cohort study. Child's Nervous System, 1-8.
- Vrettou, C. S., Drosos, E., Nepka, M., Bouboulis, G., Kalamatianos, T., Liakopoulou, C., ... & Stranjalis, G. (2022). Bacteremia Is a Risk Factor for Cerebrospinal Fluid Infection in Patients with Cerebrospinal Fluid Drains—A Retrospective Study. Bacteria, 1(1), 48-55.
- Zhou, X., & Xia, J. (2022). Application of Evans index in normal pressure hydrocephalus patients: a mini review. Frontiers in Aging Neuroscience, 13, 972.
Cite this article
-
APA : Khan, M. I., Munir, A., & Aziz, S. (2023). Association of Hydrocephalus Etiology, Infection Rate, and Age at Shunt Placement: A Retrospective Analysis of 150 Cases. Global Drug Design & Development Review, VIII(II), 41-47. https://doi.org/10.31703/gdddr.2023(VIII-II).06
-
CHICAGO : Khan, Muhammad Idris, Adnan Munir, and Syed Aziz. 2023. "Association of Hydrocephalus Etiology, Infection Rate, and Age at Shunt Placement: A Retrospective Analysis of 150 Cases." Global Drug Design & Development Review, VIII (II): 41-47 doi: 10.31703/gdddr.2023(VIII-II).06
-
HARVARD : KHAN, M. I., MUNIR, A. & AZIZ, S. 2023. Association of Hydrocephalus Etiology, Infection Rate, and Age at Shunt Placement: A Retrospective Analysis of 150 Cases. Global Drug Design & Development Review, VIII, 41-47.
-
MHRA : Khan, Muhammad Idris, Adnan Munir, and Syed Aziz. 2023. "Association of Hydrocephalus Etiology, Infection Rate, and Age at Shunt Placement: A Retrospective Analysis of 150 Cases." Global Drug Design & Development Review, VIII: 41-47
-
MLA : Khan, Muhammad Idris, Adnan Munir, and Syed Aziz. "Association of Hydrocephalus Etiology, Infection Rate, and Age at Shunt Placement: A Retrospective Analysis of 150 Cases." Global Drug Design & Development Review, VIII.II (2023): 41-47 Print.
-
OXFORD : Khan, Muhammad Idris, Munir, Adnan, and Aziz, Syed (2023), "Association of Hydrocephalus Etiology, Infection Rate, and Age at Shunt Placement: A Retrospective Analysis of 150 Cases", Global Drug Design & Development Review, VIII (II), 41-47
-
TURABIAN : Khan, Muhammad Idris, Adnan Munir, and Syed Aziz. "Association of Hydrocephalus Etiology, Infection Rate, and Age at Shunt Placement: A Retrospective Analysis of 150 Cases." Global Drug Design & Development Review VIII, no. II (2023): 41-47. https://doi.org/10.31703/gdddr.2023(VIII-II).06